Learning Outcomes:
i. Understand the concept of pointers and their role in programming.
ii. Explain how pointers store memory addresses and facilitate dynamic memory management.
iii. Recognize the benefits and uses of pointers in everyday coding scenarios.
iv. Grasp the basic operations associated with pointers for further exploration.
Introduction:
Imagine your computer's memory as a sprawling city with countless buildings (data objects). Regular variables act like street addresses, telling you where to find specific buildings. But what if you need to know not just the address, but also the key to unlock that building? That's where pointers come in, acting like little arrows on a map, pointing directly to the data itself, not just its address.
i. Memory Map Masters:
Think of a pointer as a variable containing a memory address instead of a data value. It's like holding a tiny flag with an exact number on it, indicating the location of another variable in the city of memory. By following this pointer-flag, you can access and manipulate the data directly, unlocking its secrets much faster than looking up street addresses.
ii. Dynamic Memory Management Marvels:
Pointers come in handy when dealing with data of unknown size or that needs to be created and deleted during program execution. They allow you to allocate memory dynamically, meaning on the fly, and then reuse it efficiently when you're done. Imagine building temporary houses in the city without needing fixed addresses in advance – pointers make it possible!
iii. Benefits and Beyond:
Using pointers unlocks several superpowers for your code:
Efficiency: Pointers can be faster than regular variables for accessing data directly, especially when dealing with large objects.
Flexibility: They adapt to dynamic memory allocation, making your code more fluid and responsive.
Advanced Structures: Pointers are essential building blocks for complex data structures like linked lists and trees, opening doors to powerful algorithms.
iv. Basic Operations:
Before venturing deeper, let's familiarize ourselves with some basic pointer operations:
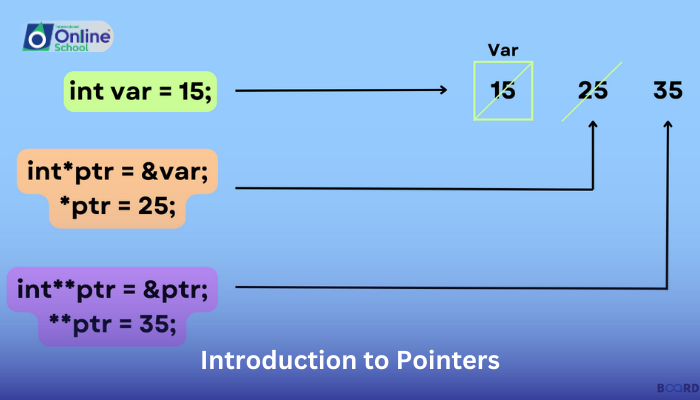
Declaring: You create a pointer variable like any other variable, but specifying its data type as a pointer to another type (e.g., int* for an integer pointer).
Assignment: You can assign memory addresses to a pointer using the & operator (e.g., pointer = &variable).
Dereferencing: You access the data pointed to by using the * operator (e.g., value = *pointer).
Example Cityscape:
Imagine you have a variable "houseNumber" storing the address of a specific house in the memory city. Now, you create a pointer "keyHolder" pointed to "houseNumber":
int houseNumber = 123;
int* keyHolder = &houseNumber;
By dereferencing "keyHolder" with "*", you access the actual value of "houseNumber" (123), unlocking the secrets of the house at that address.
Pointers might seem mysterious at first, but they're powerful tools that open doors to efficient and dynamic memory management in the programming world. This is just the beginning of your journey with pointers. Embrace their potential, explore their operations, and watch your code evolve into a well-navigated maze, where data is readily accessible and memory is used wisely. Remember, practice is key! Ask your teacher for further guidance and unleash the pointer power within your code!