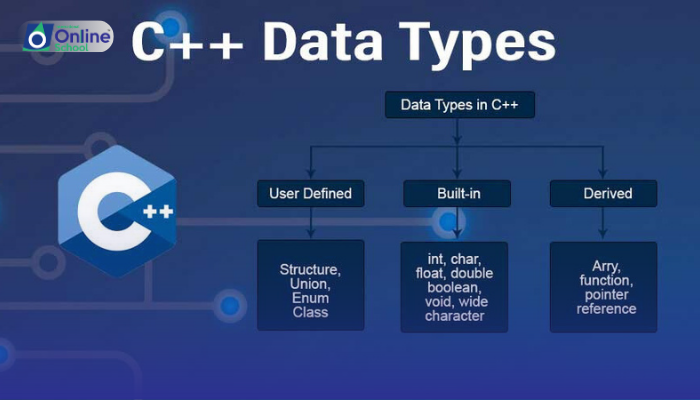
Learning Outcomes:
i. Identify the different data types available in C++.
ii. Understand the characteristics of integer types (including signed, unsigned, short, and long).
iii. Explain the range and precision of floating-point types (float) and double precision types (double).
iv. Grasp the purpose and limitations of character types (char).
Choose the appropriate data type based on the type and range of data your program needs to handle.
Introduction:
Imagine building a house, but you have only hammers and nails. Not everything gets built right, do you? Similarly, in C++, choosing the right data type is like picking the correct tool for the job. This lesson delves into the diverse toolbox of C++ data types, equipping you to select the perfect type for every piece of information in your program.
i. Integer Types: Whole Numbers for Counting and More
Think of integers as the sturdy bricks of your data house. They represent whole numbers without decimal points, used for tasks like:
Counting people at a party: int numberOfGuests = 50;
Calculating age: int myAge = 25;
Storing exam scores: int marks = 90;
C++ offers different flavors of integers:
Signed integers: Can be positive or negative (e.g., -10, 0, +5).
Unsigned integers: Always positive or zero (e.g., 0, 1, 100).
Short integers: Smaller storage space for limited ranges (e.g., -32768 to 32767).
Long integers: Larger storage space for wider ranges (e.g., -2147483648 to 2147483647).
Choosing the right size depends on the range of numbers you need to handle. Think of using a sturdy brick for a heavy wall versus a small tile for a delicate mosaic.
ii. Floating-Point Types: When Decimals Matter
For delicate tasks like measuring temperature or calculating distances, you need a more precise tool: floating-point types. These hold numbers with decimal points, like:
float pi = 3.14159; (approximation of pi)
double distance = 123.456 km; (distance with high precision)
Remember, float stores fewer decimal places than double, making it a bit faster but less accurate. Choose wisely depending on your needs!
iii. Character Types: Words Start with One Letter
Not everything in your program is a number. Characters, the building blocks of words and text, have their own type: char. Each character, like 'a', '!', or '$', occupies a single space in your data house.
iv. Choosing the Right Tool:
Think of data types as different tools in your programming toolbox. Each has its strengths and limitations:
- Use integers for counting, scores, or IDs.
- Choose floating-point types for decimals and precise calculations.
- Use characters for storing individual letters, symbols, or text snippets.
By understanding the characteristics of each data type and choosing them wisely, you'll build efficient and accurate C++ programs that handle any kind of information with ease.
Mastering C++ data types is a crucial step in your programming journey. Remember, the right tool for the job makes all the difference. Keep exploring different types, practicing choosing the appropriate ones, and soon you'll be constructing C++ programs that handle data with precision and finesse!